Understanding Pelvic Inflammatory Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
The female reproductive system is a marvel of complexity, but with that complexity comes vulnerability. Many women, at some point in their lives, may experience infections in this delicate area. While some of these infections are mild, like a vaginal yeast infection, others can be far more severe, potentially threatening a woman’s health and even her life. One such condition is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). This article will dive deep into what causes PID in females, its symptoms, treatment options, and how to protect yourself.
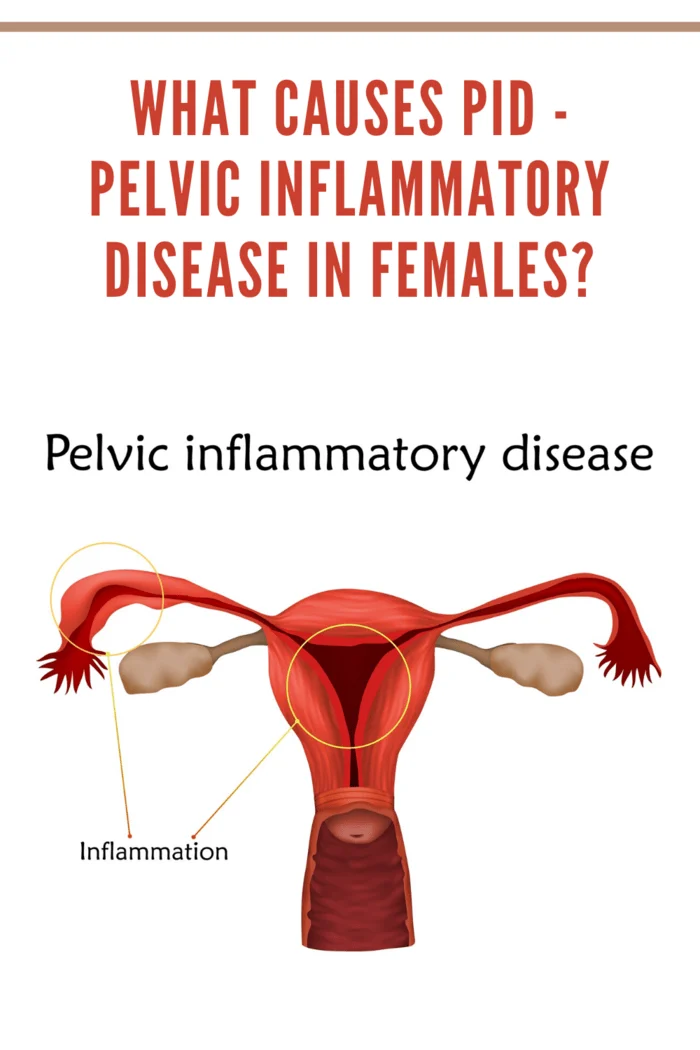
What Is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an infection that primarily affects the female reproductive organs. Caused by bacteria, most commonly those that are sexually transmitted, PID occurs when these bacteria travel from the vagina to other parts of the reproductive system, such as the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries.
What makes PID particularly insidious is that it can sometimes present without severe symptoms, making it easy to overlook. However, ignoring even mild discomfort can lead to severe consequences, including infertility. In the United States alone, it’s estimated that nearly 2% of women have dealt with PID at some point in their lives—a statistic that underscores the importance of awareness and prompt treatment.
Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of PID is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Lower Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: A persistent ache or sharp pain in this area can be a telltale sign.
- Abnormal Vaginal Discharge or Bleeding: Watch out for any unusual changes in discharge or unexpected bleeding.
- Pain During Sexual Intercourse: Discomfort or pain during sex can signal an underlying issue.
- Fever: In some cases, a fever may accompany these symptoms.
- Urination Difficulties: Pain or discomfort while urinating can also be a symptom.
- General Tiredness: Feeling unusually tired or fatigued can be linked to PID.
Symptoms can also include less obvious signs like back pain, vomiting, or nausea, which can make it challenging to connect them directly to a reproductive issue. If you’re experiencing any combination of these symptoms, it’s crucial to see a doctor immediately, even if they seem mild.
Treatment Options for PID
Treatment for PID typically involves antibiotics, but the specifics can vary depending on the severity and the underlying cause. Here’s what you need to know:
- Antibiotics: A course of antibiotics is often the first line of defense. It’s essential to complete the entire course, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
- Partner Treatment: If PID is sexually transmitted, it’s important that your partner is also treated to prevent reinfection.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary, especially if the infection has led to an abscess.
During treatment, both partners should abstain from sexual activity until the infection is completely resolved. Though symptoms may subside after a few days, following your doctor’s instructions to the letter is critical for a full recovery.
What Causes PID in Females?
The root cause of PID is bacterial infection, most commonly from sexually transmitted bacteria like gonorrhea and chlamydia. These bacteria are usually passed during unprotected sexual intercourse. However, there are other ways bacteria can enter the reproductive system:
- Childbirth or Miscarriage: The cervix is more susceptible to infection during and after childbirth or miscarriage.
- Medical Procedures: Procedures involving the insertion of medical tools into the cervix, such as an intrauterine device (IUD) insertion, can introduce bacteria.
- Immunodeficiency: A weakened immune system, perhaps due to a recent illness or antibiotic therapy, can also increase the risk.
Understanding these causes is crucial for taking preventive measures and protecting your reproductive health.

Risk Factors for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Certain behaviors and conditions can increase the risk of developing PID:
- Unprotected Sex: Engaging in sexual activity without a condom or other protective measures heightens the risk.
- Multiple Sexual Partners: Having multiple partners increases the likelihood of encountering sexually transmitted bacteria.
- History of Pelvic Infections: Previous infections can make the reproductive system more susceptible to future issues.
- Vaginal Douching: This practice can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, making it easier for harmful bacteria to thrive.
- Intrauterine Device (IUD): While generally safe, the insertion process of an IUD can occasionally introduce bacteria.
Being aware of these risk factors can help you make informed decisions about your sexual health and hygiene.
Complications of Untreated PID
If left untreated, PID can lead to several severe complications, including:
- Infertility: Damage to the fallopian tubes can prevent conception.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: The risk of a pregnancy occurring outside the uterus increases, which can be life-threatening.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain in the pelvic region can become a long-term issue.
These complications underscore the importance of early detection and treatment of PID.

Prevention: Protecting Your Reproductive Health
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to something as serious as PID. Here are some tips to safeguard your reproductive health:
- Practice Safe Sex: Always use condoms and have open conversations with your partner about sexual health.
- Regular Testing: Regular screenings for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can catch problems early.
- Avoid Douching: Stick to natural cleaning methods, as douching can disrupt the vagina’s natural flora.
- Choose Natural Materials: Opt for breathable, natural fabrics in your underwear to reduce the risk of irritation and infection.
- Regular Check-Ups: Keep up with routine gynecological exams, especially if you’re sexually active.
Take Control of Your Health
Taking proactive steps in your reproductive health is essential. Consider regular screenings for STIs and ensure that you and your partner practice safe sex. You can explore reliable, doctor-recommended products that support sexual health. Check out this Amazon link for a selection of products designed to help maintain your reproductive well-being.
This detailed and personalized guide aims to empower you with the knowledge needed to understand, prevent, and manage Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. While we are not doctors, remember, your health is in your hands, so take the steps necessary to protect it.
